|
Dew Math for .NET
|
|
Dew Math for .NET
|
Poisson probability density function (PDF).
|
Parameters |
Description |
|
int x |
Function domain, positive integer or zero. |
|
double Lambda |
Distribution parameter, real positive value. |
the Poisson probability density function (PDF) for value x using the parameter Lambda. Lambda must be positive, otherwise the result is NAN.
The Poisson probability density function is defined by the following equation:
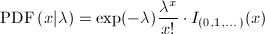
Poisson random variable usually arise in connection with what are called Poisson processes. Poisson process involve observing discrete events in a continuous interval of time, length or space. The variable of interest in a Poisson process is the number of occurrences of the event in an interval of length. Basically, the result is physically, the parameter Lambda of a Poisson process represents the average number of occurrences of the event in question per measurement unit.
One other important application of the Poisson distribution is approximating the BinomPDF distribution with the Poisson distribution. This approximation is usually good if n >= 20 and p <= 0.05 (binomial distribution parameters) and very good if n >= 100 and np <= 10. Since the approximation is used when number of events (n) is large and p (probability of success) is small, the Poisson distribution is often called the distribution of "rare" events.
|
Copyright (c) 1999-2024 by Dew Research. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|