|
Dew Math for .NET
|
|
Dew Math for .NET
|
Normal probability density function (PDF).
|
Parameters |
Description |
|
double x |
Function domain, real value. |
|
double Mu |
Distribution location parameter, real value. |
|
double sigma |
Distribution scale parameter, real positive value. |
the normal probability density function (PDF) for value x using the parameters Mu (mean value) and sigma (standard deviation). Sigma must be positive value, otherwise the result is NAN.
The normal probability density function is defined by the following equation:
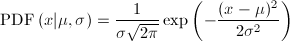
where Mu is mean value and sigma is standard deviation. Special case of normal distribution (mean = 0, sigma =1) is called standard normal distribution.
The normal distribution is a distribution that underlies many of the statistical methods used in data analysis. This distribution is often referred to as "Gaussian" distribution. Normal distribution can be used for modeling when the sample size is large. The theoretical justification can be found in Central Limit Theorem which states (roughly) that the sum of independent samples from any distribution with finite mean and variance converges to the normal distribution as the sample size goes to infinity.
|
Copyright (c) 1999-2024 by Dew Research. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|