Pearson correlation coefficients.
procedure CorrCoef(const X: TDenseMtxVec; const Y: TDenseMtxVec; const aResult: TMtx); overload;
|
Parameters |
Description |
|
X |
Defines first sample (variable) values (observables). |
|
Y |
Defines second sample (variable) values (observables). |
|
aResult |
Returns Pearson correlation coefficients bewteen samples X and Y. Size of Result is adjusted automatically. |
Calculates Person correlation coefficients between X and Y representing two samples/variables with X and Y Values being treated as observables.
If X and Y are two matrices, the rouitine calculates Pearson correlation coefficients rx,y between X and Y matrix. The algorithm assumes X and Y are two samples (variables) and all X are are treated as it's observables (same goes for Y).
Correlation coefficient
The correlation coefficient rho between two random variables is defined by the following equation:
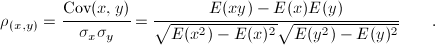
where x,y are two variables, Cov covariance betwen x and y, sigma(s) their expected standard deviations and E-s their expected values. If the variables are independent then the correlation is 0, but the converse is not true because the correlation coefficient detects only linear dependencies between two variables.
Sample correlation coefficients.
If we have a series of n measurements of X and Y, then the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient can be used to estimate the correlation of X and Y. The Pearson coefficient is also known as the "sample correlation coefficient". The Pearson correlation coefficient is then the best estimate of the correlation of X and Y .
The correlation is defined only if both of the standard deviations are finite and both of them are nonzero.
Calculate correlation coefficients from Data1 and Data2 representing two variables.
Uses MtxExpr, Statistics; procedure Example; var Data1, Data2: Vector; CorrMtx : Matrix; begin Data1.SetIt(False,[1,2,3]); Data2.SetIt(False,[5,5.5,1]); CorrCoef(Data1,Data2,CorrMtx); // CorrMtx = [1.00000000, -0.81088485, // -0.81088485, 1.00000000] end;
#include "MtxExpr.hpp" #include "Statistics.hpp" void __fastcall Example() { sVector data1,data2; sMatrix corr; data1.SetIt(false,OPENARRAY(double,(1,2,3))); data2.SetIt(false,OPENARRAY(double,(5,5.5,1.0))); CorrCoeff(data1,data2,corr); // corr = [1.00000000, -0.81088485, // -0.81088485, 1.00000000] }
|
Copyright (c) 1999-2025 by Dew Research. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|